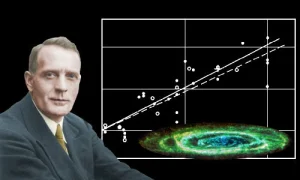
Edwin Hubble was the originator of the expansion theory of the universe and the father of modern astronomy. Hubble was one of the leading astronomers of the 20th century. The Hubble Space Telescope was named after him. His discovery of countless galaxies beyond our own Milky Way in the 1920s revolutionized the understanding of the universe and our existence within it.
Edwin Hubble (1889–1953) was born in Marsfield, Missouri. He was moved to Wheaton, Illinois before his first birthday. He studied mathematics and astronomy at the University of Chicago and earned a Bachelor of Science degree in 1910. He was one of the first Rhodes Scholars at the University of Oxford, where he studied law. After serving briefly in World War I, he returned to the University of Chicago and earned his doctorate in 1917. He died of a heart attack on September 28, 1953, in San Marino, California, after a long career at the Mount Wilson Observatory.
Most astronomers of Hubble’s time thought that the entire universe, complete with planets, countless stars and nebulae, was contained within the Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy itself had become synonymous with the entire universe. In 1923, Hubble trained the Hooker telescope on a faint band of sky called the Andromeda Nebula. They found that Andromeda is also full of stars like our Milky Way, but only fainter stars. They saw a star there that belonged to a Cepheid variable, a type of star of variable brightness that can be used to measure distances. This helped Hubble to conclude that the Andromeda Nebula was not a nearby star cluster but an entire galaxy, now called the Andromeda Galaxy. In later years he made similar discoveries with other nebulae. By the end of the 1920s, most astronomers were convinced that our Milky Way galaxy was not alone but one of millions of galaxies in the universe. This discovery proved to be a turning point in changing the way we think about the understanding of the universe.
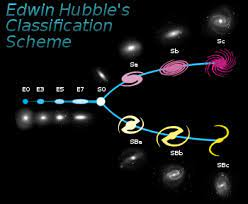
Hubble went a step further. By the end of that decade, they had discovered enough galaxies to compare with each other. He created a system for classifying galaxies into elliptical, spiral and barred spiral. This system is called the Hubble tuning fork diagram, an evolved form of which is used today.
But the most surprising discovery resulted from Hubble’s own study of the spectra of 46 galaxies, and specifically the Doppler velocities of those galaxies relative to our own Milky Way galaxy. Hubble found that the more distant the galaxies are, the faster they are moving away from each other. Based on this observation, Hubble concluded that the universe is expanding uniformly. Many scientists had also introduced this theory on the basis of Einstein’s general relativity. But Hubble data published in 1929 helped reassure the scientific community.
Hubble and his colleague on Mount Wilson, Milton Humson, estimated the rate of expansion of the universe at 500 kilometers per second per megaparsec (one megaparsec, or a distance of one million parsecs, is approximately equal to 32.6 million light-years, so one megaparsec is A galaxy two megaparsecs away will be moving away from us twice as fast as the Milky Way). This estimate is called the Hubble constant.
Big Bang Theory and Edwin Hubble
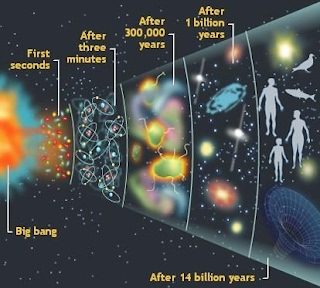
In 929 Edwin Hubble made a surprising discovery, he found that galaxies and other celestial bodies are rapidly moving away from each other in any direction you look in space. In other words the universe is expanding. This means that in history all matter in the universe may have been much closer to each other than it is today. And there must have been a time when all the celestial bodies would have been in one place. Astronomers have tried to analyze the circumstances of how cosmic matter is so close to each other. This dot was a very small dot, of extreme density. This point form of the universe must have been extremely hot due to its extreme density. In this situation no law of physics, mathematics or science works. This is the condition when man is unable to estimate or analyze in any way. Time or time also stops in this situation, in other words time and time do not matter. In this situation, for some unknown reason, suddenly the expansion of the universe started. With a big bang the universe was born and the matter in the universe started moving away from each other. This theory was named Big Bang Theory, which is the most accepted theory related to the birth of the universe.
hubble space telescope
One of the main goals of the Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, is the correct interpretation of the Hubble constant. In 2001, a team studying the supernova with ground-based optical telescopes, as well as Hubble, established a rate of 72 ± 8 km/s/megaparsec. In 2006, a team studying the cosmic microwave background with NASA’s WMAP satellite improved this measurement to 70 km/s/megaparsec. With the help of the Hubble telescope, it was also found that not only is the universe expanding, the expansion is also accelerating. The mysterious force responsible for this acceleration is termed as invisible energy.

The Hubble telescope revolutionized astronomy, changing our understanding of the universe. Hubble has made us aware of many new facts about the beginning and age of the universe. Its latest achievement is gathering evidence about the age of the universe.
With the help of Hubble, a team of astronomers has discovered a group of stars believed to be the oldest moving towards an energyless state 7000 light years away. Based on the rate of extinction of these stars, the age of the universe has been estimated between 13 and 14 billion years. Apart from this, during the last 12 years, this telescope has also provided thousands of attractive pictures of distant celestial objects.
About a hundred years ago, astronomers in America began to build large telescopes based on reflectors. One of those telescopes had a 100-inch Mount Wilson reflector, which was considered one of the greatest scientific achievements of the time. That huge telescope was established by an astronomer named Edwin Hubble, in whose honor the first space telescope was called the Hubble telescope. With the help of his telescope, Edwin Hubble proved that the universe is continuously expanding. His discovery is known in astronomy as Hubble’s law.
Later, the curiosity to know the age of the universe inspired astronomers to build bigger telescopes and telescopes with reflectors of 200 inches size were also made. But they needed a telescope that was unaffected by the interference of Earth’s atmosphere, and thus the space telescope was born. But this dream of astronomers became a reality in 1990, when the Discovery shuttle carried the Hubble telescope into space.
However, work on this telescope, which realized the dreams of astronomer Edwin Hubble, had started in the US in the 1970s itself. The Hubble telescope was developed at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, USA. Space traffic halted for a few years following the accident of the US space shuttle Challenger, disrupting the Hubble project.The much larger size of the Hubble Space Telescope was envisaged, but it ultimately proved to be a telescope with a reflecting surface only 96 inches in size. But being in space away from the atmosphere, the Hubble telescope is proving to be more effective than much larger telescopes available on Earth.
It has been regularly serviced. For this, astronauts are taken to Hubble with the help of spacecrafts of the American space agency NASA.
technical facts
- NASA has spent about two and a half billion dollars to install the Hubble telescope in space. Its one servicing costs about $ 500 million.
- The Hubble orbiting 600 km above the surface of the earth weighs 11 tonnes. It takes about 100 minutes to make one round of the earth.
- Its length is 13.2 meters and maximum diameter is 4.2 meters.
- The Hubble telescope collects 10 to 15 gigabytes of data per day.
- After the last servicing mission completed in the year 2009, it is expected to continue working till the year 2030-40.
Finally, Edwin Hubble lived up to his name with a telescope that changed our understanding of the universe. His spirit of discovery lives on today in the form of the Hubble Space Telescope.